How to Make a Pogo Pin
Pogo pins are precision spring-loaded connectors designed for temporary, high-reliability electrical connections. They are widely used in applications such as testing, programming, and connectors for boards in mobile devices, computers, and other electronics.
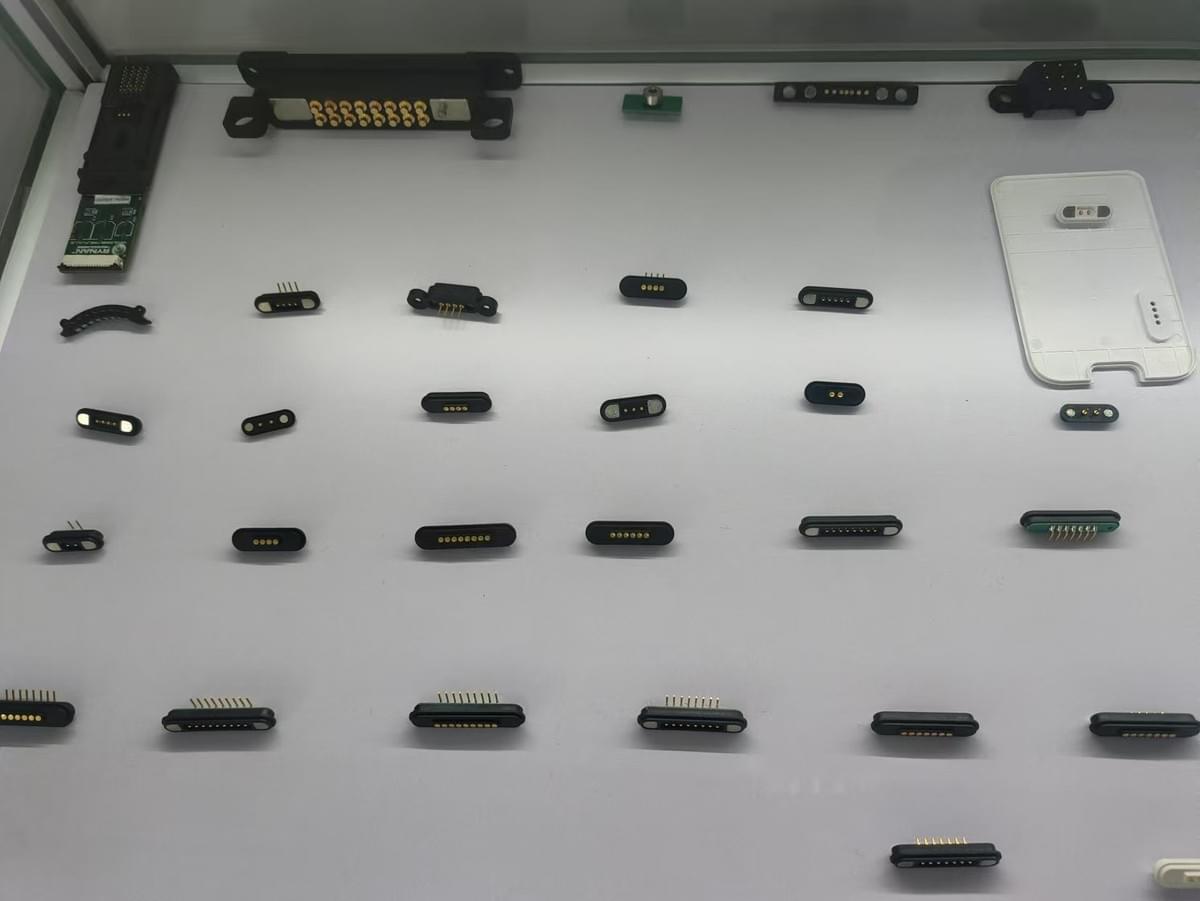

To make a pogo pin, follow these key steps:
1.
Select the Material
The main materials for a pogo pin include:
- Pin body: Typically made from stainless steel or brass, providing strength and corrosion resistance.
- Spring: Usually made from phosphor bronze or stainless steel. The spring must have the right tension to ensure the pin makes solid contact but still has enough flexibility.
- Ball: At the tip of the pogo pin, there’s often a small ball made from stainless steel or tungsten for improved durability and better contact.
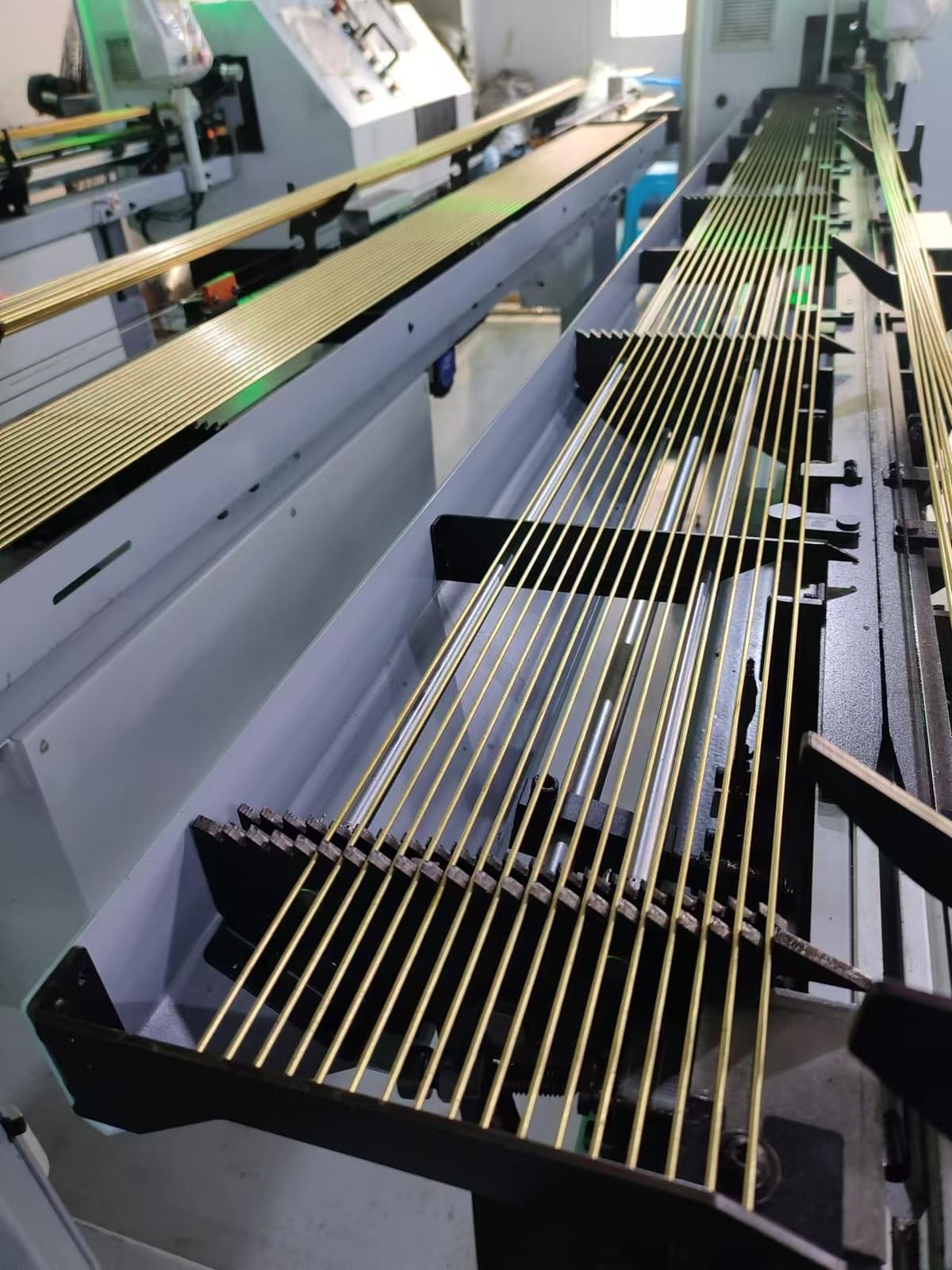

2.
Fabricate the Pin Body
The pin body is made using precision machining or stamping processes. It is often cylindrical with a hollow section near the base where the spring will sit. In the process:
- Cutting: The pin is cut to the desired length using CNC machines or stamping methods.
- Deburring: After cutting, any sharp edges or burrs are removed.
3.
Make the Spring
The spring for a pogo pin is critical for its functionality. The spring must have enough tension to push the pin out but also compress when it makes contact with the circuit. Springs are:
- Formed from wire: The wire is coiled to the desired spring shape.
- Tempered and heat-treated: To ensure durability and the correct spring rate (how much force is needed to compress it).
4.
Assembly of Spring and Pin
The spring is carefully inserted into the hollow section of the pin body. The tension of the spring ensures the pin will stay extended until it comes into contact with another surface. Precision is crucial to ensure the pin compresses correctly without losing the necessary force.
5.
Attach the Contact Tip
The ball or contact tip is often attached to the end of the pin using press fitting or soldering. The tip may be a ball bearing or a flat, highly conductive surface designed for maximum electrical contact.
6.
Testing and Quality Control
After assembly, each pogo pin must be tested for:
- Spring force: Ensuring that the spring compresses and extends correctly.
- Electrical conductivity: Verifying that the pin provides a stable and reliable electrical connection.
- Durability: Conducting tests to check the pin’s resistance to wear and tear, particularly with repetitive use.
7.
Final Inspection
The finished pogo pins are subject to visual and mechanical inspection. This ensures they meet specifications for dimensions, strength, and functionality. Automated systems or manual checks can be used to verify the quality before they are packaged and sent for use.
Common Applications of Pogo PinsPogo pins are often used in:
- Testing Fixtures: For connecting to test boards and prototypes.
- Charging Connectors: In devices such as smartphones and wearables.
- Programming Jigs: For flashing firmware onto devices.
By following these precise manufacturing steps, you can create reliable pogo pins that ensure efficient, high-quality electrical connections in a variety of applications.